The Human Brain
The human brain is the main organ of the human central nervous system. It is located in the head, protected by the skull. It has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but with more developed cerebral cortex.

The adult human brain weighs about 1.3 - 1.5 kg (2.9 - 3.3 lb), or about 2% of total body weight with a volume of around 1130 cm cubic centimetre in woman and 1260 cm cubic centimetre in men.
How Your Brain Works

Click the video to play :
The brain is the control center of the body It contains thoughts, memory, speech and movement. It controls how many of your organs work. When the brain is healthy, it works quickly and automatically.The brain is the most complex part of the human body. All of the parts of the brain work together, but each part has its own special duties.
Learn more:
National Institute of Mental Health
PARTS AND FUNCTIONS :
front of brain, controls speech production, emotional behaviors, makes decisions, motor cortex initiates movement
Occipital lobes
back of brain, visual cortex, info from right visual field processed in left visual cortex and vice versa
Temporal lobes
hearing,wernickes area in left lobe, understands language, right lobe understands music, above ears
Hemispheres
right and left hemispheres divide brain in half
Forebrain
controls thought and reason, hippocampus, hypothalamus, thalamus, amygdala make up this part
Midbrain
coordinates simple movements with sensory info, reticular formation
Hindbrain
life support system, made of medulla, pons, cerebellum, brainstem
Fissures
seperate 4 lobes, folds
Pituitary gland
pea sized, in core of brain, controlled by hyppothalamus, releases hormones that influence growth, sex hormones
Cerebellum
baseball sized, extends from rear of brainstem, 2 halves, helps judge time, modulate emotions, discriminate sounds and textures,coordinates movement, balance
Cerebral cortex
covers cerebellum hemispheres like bark, neural cells, thinking crown, sensory info, high level thinking
Corpus callosum
wide band of axon fibers connecting 2 hemispheres of brain, carry messages between them
Hippocampus
enables formation of new long term memories, above pituitary to left next to amygdala
Hypothalamus
controld body temp, heartrate by controlling medulla, sets appetite, emotional state, hormones, biological rythms, bellow thalamus above pituitary
Lymbic system
made of amygdala. hypothalamus btwn brains older parts and cerebral hemispheres
Medulla
swelling of brainstem, controls heartbeat and breathing
Pons
coordinate movement, above medulla, arousal
Associations areas
regions of cerebral cortex with no specific function but involved in high mental functions
Reticular formation
inside brainstem, btwn ears, network of neurons extending to thalamus, sensory info travels through, involved in arousal
Brocas area
left frontal lobe,ability to speak or expressive aphasia
Wernickes area
left temporal lobe,ability to comprehend written and spoken language or receptive aphasia
Motor cortex
strip down middle of cortex in rear of frontal lobes, left side controls right body movements vice versa
Sensory cortex
strip behind motor corex, front of parietal lobes, recieves info from skin senses and movement senses of body
Thalamus
top of the brainstem, joined pair of egg shaped structures, recieves info from all senses except smell snf routes it to higher brain regions that deal with that sense
Amygdala
two bean sized neural clusters next to hypocamupus on both sides, influences aggresion and fear
Visual cortex
un occipital lobe, reconstructs visual images
Auditory cortex
in both temporal lobes, center for hearing
Dendrites
branching tubular processes that recieve info and conducts it to cell body
Axon
emerges from cyton and branches into terminal buttons sends info from dendrites to other neurons
Myelin sheath
formed by glial cells, covers axon, insulates, helps speed process, increases as get older
Glial cells
make up myelin sheath
Action potential
brief electrical charge that travels down axon, a rush of ions into neuron after its resting period
Resting potential
neurons arent transmitting or recieveing info, inside is negative outside axon is positive
Depolorization
causes next axon to open, internal charge changes to positive and is same as outside, change in charge produces action potential
Refractory period
neuron pumps sodium outside and then fires again
Terminal buttons
recieve info from axon
Sensory neurons
recieve info that go to brain and spinal cord
Motor neurons
carry outgoing messages from brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands
Peripheal nervous system
sensory and motor neurons connect to central nervous system to rest of body
Somatic nervous system
part of peripheal, controls skeletal muscles
Sympathetic nervous system
division of autonomic, arouses body, mobilizes in stressful situations, unvoluntary, fight or flight
Parasympathetic nervous system
calms body after an emergency and after sympathetic nervous system works
Autonomic nervous system
non voluntary movements
Excitory neurotransmitters
cause next neuron to fire
Inhibitory nerotransmitters
prevent next neuron from firing
Adrenal glands
release adrenaline, increase heart rate, blood pressure
Afferent neurons
go to brain
Efferent neurons
exit brain
Acetocholine
enables muscle action, learning, memory
Alzheimers disease
caused by deterioration of acetocholine producing neurons
Dopamine
influences movement,learning,attention,emotion, pleasure and reward system
Schizophrenia
excess dopamine
Parkinsons disease
lack of dopamine produces tremors and decreaseed mobility
Serotonin
affects mood,hunger,sleep,arousal
Depression
lack of serotonin. prozac medication
Norepinephrine
controls alertness and arousal
Depressed mood
lack of norepinephrine
Glutamine
involved in memory, excitatory neurotransmitter, oversupply causes migrains or seizures
Plasticity
brains ability to form new connections that take over for damaged part
Right brain
simple spatial reasoning
Left brain
produces speech and understands it
Interneurons
only in central nervous system
ELectroencephalogram
amplified reading of waves produced by electrical activity in the brain, ataches things to the head
PET
consumes radioactive glucose and it shows where brain is most active
MIR
magnetic field, aligns spinning of atoms, when atoms return to normal spin they release signals that provide detailed picture of brain tissues
MRI
reveals structure and function, shows brain functions by blood movement to that part
The development
During the first three weeks of gestation, the human embryo's ectoderm forms a thickened strip called the neural plate. The neural plate then folds and closes to form the neural tube. This tube flexes as it grows, forming the crescent-shaped cerebral hemispheres at the head, and the cerebellum and pons towards the tail.
|
In Psychology, the human brain is separated into two parts :

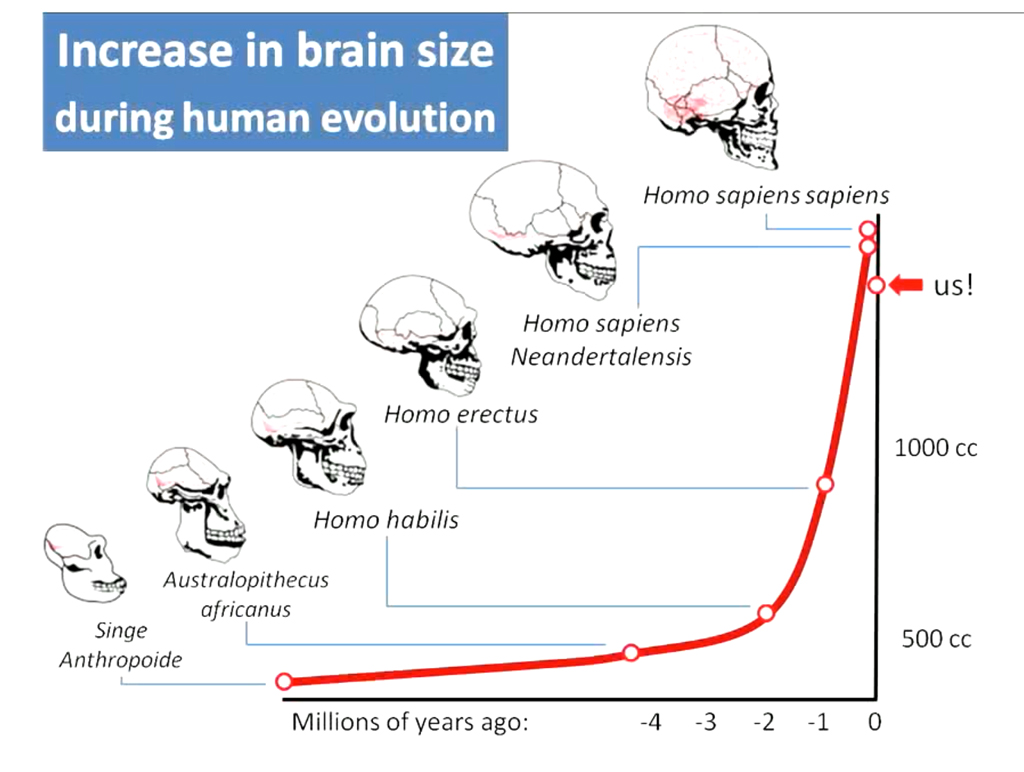
The Evolution of the Human Brain
John Hawks, a professor of anthropology at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, answers:
Humans are known for sporting big brains. On average, the size of primates' brains is nearly double what is expected for mammals of the same body size. Across nearly seven million years, the human brain has tripled in size, with most of this growth occurring in the past two million years.
Determining brain changes over time is tricky. We have no ancient brains to weigh on a scale. We can, however, measure the inside of ancient skulls, and a few rare fossils have preserved natural casts of the interior of skulls. Both approaches to looking at early skulls give us evidence about the volumes of ancient brains and some details about the relative sizes of major cerebral areas. ...
So there you go guys, a few things for me to share about the human brain. I wish you learned and know more about the thing living inside your thick skull.
Facts about the Human Brain :
1. Lack of oxygen in the brain for 5-10 minutes results in permanent brain damage.
2. the human brain keeps developing until late 40s
3. The human brain is the only organ in the human body that lacks nerves despite the fact that it acts as the central command for the central nervous system. This simply implies that, the human brain feels no pain.
4. When awake, the human brain produces enough electricity to power a small light bulb.
5. The pathogist who made Einstein body autopsy stole his brain and kept it in the jar for 20 years.
6. 60% of your brain is fat.
7. Dieting can cause the brain to eat itself scientist say.
8. The smell of chocolate increases theta brain waves, which triggers relaxation.
9. Forgetting is good for the brain.
10. When you learn something new, the structure of the brain changes.
11. You have 70,000 thoughts a day.
THANKS FOR STOPPING BY
Credits/sources :
http://kids.niehs.nih.gov/games/riddles/brain.htm
https://quizlet.com/6867974/brain-parts-and-functions-psychology-flash-cards/
http://www.scientificamerican.com/article/how-has-human-brain-evolved/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_brain


No comments:
Post a Comment